Designations Of U.S. Military Aero Engines
Copyright © 2000-2024 Andreas Parsch
3 Jet and Turbine Engines, 1946 - 1968
5 The Current System (MIL-STD-1812A)
-
5.1 Air-Breathing Engines
5.2 Rocket Engines
6 Sources
1 Introduction
For the engines of its first aircraft, the US military services used the manufacturers' names. Soon after World War I, however, more formal designation systems were devised not only for the aircraft themselves but also for their engines. When jet, turbine and rocket engine development started at the end of World War II, formal designations were assigned to these types of engines almost from the beginning. In the last decades, however, there is a trend towards using manufacturers' designations again for engines which were not developed specifically for the military.
The following graph shows the various documents and standards used to define the aero engine designation systems. A bold black arrow indicates, that the system underwent no or only minor changes, when defined in a new document. A light gray arrow indicates a major change, i.e. the designation system was superseded by a completely different one.
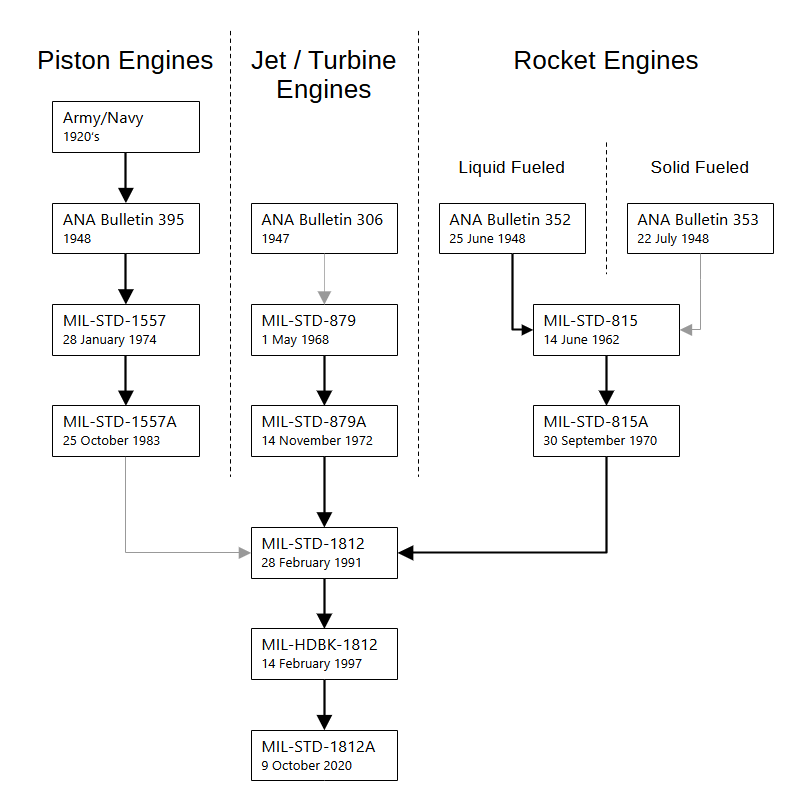
This article explains the various engine designation systems and lists all aircraft and missile engines,
which received a military designation, and the aircraft or missiles which used them.
Because the focus of the article is on the designations, I don't try to give specific details for the engines
(like power rating, etc.). These details can differ significantly
between models of the same basic engine anyway.
For each engine type, I try to provide a complete list of US military
aircraft, which used this engine. To keep these lists reasonably short, I use the following terse format for an aircraft type:
- (Number of engines)Military Designation
Usually only the basic designation (without specific model letters or numbers) is given. That means, that all - or almost all - models of this type used the engine. Exceptions are listed as users of the approriate alternate engine. If an entry is in brackets, the type was planned to use the engine, but not a single example was completed before the aircraft and/or engine was cancelled. Additionally, each list of aircraft designations is headed by a descriptor of the designation system used.
2 Piston Engines
Since the early 1920's, piston engines are designated by a system based on cylinder arrangement and total piston displacement. This designation system was later formally defined in Air Force/Navy Aeronautical (ANA) Bulletin 395, which was replaced by MIL-STD-1557 on 28 January 1974. The latter document was superseded by the current MIL-STD-1812 on 28 February 1991.
| Examples: | V | - | 1650 | - | 7 | ||
| R | - | 4360 | - | 35 | C | ||
| X | O | - | 470 | - | 5 | ||
| (5) | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
The letter (1) indicates the cylinder arrangement of the engine:
- H - Double Opposed
- IV - Inverted Vee
- L - In-Line
- O - Opposed
- R - Radial
- V - Vee
Optionally, the letter could be prefixed by one of the modification letters:
- D - Diesel Engine
- G - Geared Engine
MIL-STD-1557 dropped all letters and prefixes, except O, R and V, and added the designator
- RC - Rotating Combustion
The number (2) is the total piston displacement of the engine, rounded to the next 5 cubic inches.
(3) is the model number for a particular version of the engine. The Army and Air Force used odd numbers from 1 up, while the Navy used even numbers from 2 up. In MIL-STD-1557, this was revised. The Air Force was assigned model numbers 100 to 399, the Navy 400 to 699 and the Army 700 to 999. This was done to match the procedure for jet/turbine model numbers defined by MIL-STD-879.
(4) is an optional letter for designating minor modifications of an engine model. Letters are assigned alphabetically from A on (I and O are not used). The letter W is reserved for engines with water injection. In MIL-STD-1557, the letter T was reserved for training (i.e. non-flying) engines. T could be combined with other letters, e.g. the training version of the R-1830-92A engine would be designated R-1830-92AT.
(5) is an optional status prefix:
- X - Experimental
- Y - Service Test
- Z - Obsolete
This designation system could lead to the same basic (arrangement - displacement) designation for
two different engines. E.g., the Liberty 12 engine of the 1920s and the Merlin engine of WW II were
both officially known as V-1650. However,
I don't know any case, where this occured for contemporary
engines, so this did not pose problems in "real life".
(It is also possible, that the displacement was sometimes rounded to the next 10 cubic inches to get different
designations for engines with similar displacement.)
Note: While this system was theoretically revised by MIL-STD-1812, it is - to all intents and purposes - still in use today, mainly because of two reasons:
- Existing engines are not redesignated and there is no new piston engine development specifically for the military.
- Many manufacturers of commercial engines (e.g. Lycoming and Continental) designate their engines according to the "arrangement-displacement" system, which makes it very convenient for the military to use these commercial designations, when such an engine is procured.
Designation List:
| Designation | Manufacturer and Model | Remarks; Aircraft |
|---|---|---|
| H-2470 | Lycoming XH-2470-1 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)P-54 Navy(1922-1962): (1)F14C-1 |
| H-2600 | Pratt & Whitney X-1800-SA2G | |
| H-3730 | Pratt & Whitney | |
| H-4070 | Menasco XH-4070-1 |
| IV-1430 | Continental XI-1430-1 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)P-49, [(1)P-52], [(1)P-53], (2)P-67 |
| IV-2040 | Menasco XIV-2040-1 | |
| IV-2220 | Chrysler XIV-2220-1 |
| L-330 | Martin | |
| L-365 | Menasco Pirate C-4 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)PT-20 Navy(1922-1962): (1)JH |
| L-375 | DeHavilland Gipsy Major | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)PT-24 |
| L-390 | Ranger 6-390-B | |
| L-410 | Ranger 6-410-B2 | |
| L-440 | Ranger 6-440-C2 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)UC-61K, (1)XUC-86A, (2)OA-14, (2)PG-2, (1)PT-19, (1)PT-26 Navy(1922-1962): (2)J4F, (1)J2K, (1)NR |
| L-510 | Miller Double 4-255 | Army/AF(1924-1962): [(1)P-57] |
| L-825 | Liberty 6 | Army(1919-1924): (1)PN-1 |
| O-15 | Righter |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)OQ-2, (1)OQ-3, (1)OQ-7, (1)OQ-13 Navy(1922-1962): (1)TDD |
| O-40 | Muncie Gear | |
| O-45 | Righter/Kiekhaefer |
Army(1924-1962): (1)OQ-6, (1)OQ-14, (1)OQ-15, (1)OQ-16, (1)OQ-17 Navy(1922-1962): (1)KD3G, (1)KD4G, (1)KDR, (1)TDD-3/4 |
| O-90 | McCulloch |
Army(1924-1962): (1)OQ-6A, (1)OQ-19 Navy(1922-1962): (1)KD2R |
| O-100 | McCulloch |
Navy(1922-1962): (1)KD6G, (1)KD2R-3/5 Missiles: (1)MQM-33, (1)MQM-36 |
| O-145 | Lycoming O-145-B2 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)UC-90A, (1)C-92, (1)C-95, (1)L-2D/F/J, (1)L-3G/H, (1)L-4C/G |
| O-150 | Franklin 4-AC-150 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)L-2E/G/K/L |
| O-170 | Continental A-65 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)C-83, (1)UC-90, (1)L-2, (1)L-3, (1)L-4, (1)L-8, (1)O-54,
(1)O-55, (1)O-57(L-2), (1)O-58(L-3), (1)O-59(L-4) Navy(1922-1962): (1)NE |
| O-175 | Franklin 4-AC-176-B2 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)L-3D, (1)L-4D |
| O-180 | Franklin 4-AC-176-F3 | |
| O-190 | Continental C-85 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)L-16 |
| O-200 | Franklin 4-AC-199-E4 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)C-65, (1)L-6, (1)L-7, (1)L-9, (1)O-63(L-6), (1)PQ-8 Navy(1922-1962): (1)XTDC-1 |
| O-200 | Continental (Teledyne) O-200-A | Joint(1962+): (1)X-26B |
| O-205 | Continental | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)L-16B, (1)L-18 |
| O-235 | Lycoming O-235-A | Navy(1922-1962): (1)AE, (1)HE(AE) |
| O-235 | Lycoming (Textron) O-235-L2C | Joint(1962+): (1)TG-7, (1)RG-8 |
| O-290 | Lycoming O-290-B |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)C-107, (1)H-24, (1)L-14, (1)L-15, (1)L-21(U-7), (1)PQ-8A, (1)R-9 Navy(1922-1962): (1)TDC Joint(1962+): (1)U-7 |
| O-300 | Franklin 6-AC-298-F3 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): [(1)PQ-9], [(2)PQ-10], (1)PQ-13, (1)PQ-14 Navy(1922-1962): (1)TD2C |
| O-335 | Aircooled Motors (Franklin) |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)H-13, (1)H-23, (1)H-30, (1)T-35 Navy(1922-1962): (1)HTE, (1)HTL-1/3/5, (1)HUM |
| O-360 | Lycoming | Joint(1962+): (1)H-55 |
| O-360 | Continental | Joint(1962+): (2)O-2, (1)O-3, (1)T-41, (1)XV-8A |
| O-405 | Franklin 6-ACV-405 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)BQ-1, (1)XUC-86B, (1)PQ-15, (1)R-6, [(1)R-7], (1)R-8 Navy(1922-1962): (1)HOS, (1)TD3C |
| O-425 | Franklin 6-AC-425 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)H-18, (1)L-13, [(1)OA-15] |
| O-435 | Lycoming O-435-A |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)XBQ-2, (2)BQ-4, (1)H-13H/J/L/M/N/P/Q/S/T, (1)H-22, (1)L-5, (1)L-22(L-17D),
(2)L-23(U-8), (1)L-24, (1)L-26(U-9), (1)O-62(L-5), (1)PT-25, (1)PQ-12 Navy(1922-1962): (1)HO5S, (1)HTK, (1)HTL-2/4/6/7(H-13), (1)HUL(H-13), (1)OY, (2)TDR Joint(1962+): (2)U-8, (1)U-9B |
| O-470 | Continental |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)L-17(U-18), (1)L-19(O-1), (2)L-27(U-3), (1)T-34A/B Navy(1922-1962): (1)OE(O-1) Joint(1962+): (1)O-1, (2)U-3, (1)U-17, (1)U-18 |
| O-480 | Lycoming GO-480-B2 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)L-23D/E/F(U-8), (1)L-26B/C(U-4,U-9), (1)L-28(U-10) Joint(1962+): (1)U-4B, (2)U-8D/E/F, (1)U-9C, (1)U-10 |
| O-520 | Continental | Joint(1962+): (2)C-28, (2)T-42, (1)U-17B, (1)U-22, (1)U-26 |
| O-540 | Franklin 8-ACGSA-538 | |
| O-540 | Lycoming (Textron) |
Navy(1922-1962): (2)UO(U-11) Joint(1962+): (1)T-3, (2)U-11 |
| O-550 | Continental (Teledyne) GIO-550A | Joint(1962+): (2)U-38 |
| O-805 | Franklin 12-ACGSA-806 | Army/AF(1924-1962): [(2)BQ-5] |
| O-580 | Lycoming | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)H-31 |
| O-1230 | Lycoming O-1230-A | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)XA-19A |
| R-250 | General Motors X-250-D | |
| R-265 | Ken-Royce LeBlond 5-G | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)UC-102 |
| R-270 | Lambert | |
| R-370 | Ken-Royce LeBlond 7-G | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)UC-102A |
| R-370 | Kinner K-5 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)PT-6, (1)PT-7 Navy(1922-1962): (1)N2Y |
| R-420 | Warner Scarab | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)C-10 |
| R-440 | Kinner B-5 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)PT-16, (1)PT-20A, (1)PT-21 |
| R-500 | Warner Super Scarab |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)C-61, (1)UC-77C/D, (1)C-80, (1)C-94 Navy(1922-1962): (1)GK |
| R-540 | Kinner R-5-2 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)PT-22 |
| R-540 | Wright Whirlwind 5 (J-6) | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)YPT-9, (1)YPT-10/B |
| R-545 | Continental A-70 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)YPT-9A, (1)YPT-10A, (1)Y1PT-11 |
| R-550 | Warner Super Scarab | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)R-4 |
| R-600 | Curtiss Challenger | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)PT-5, (1)Y1PT-11A |
| R-670 | Continental R-670-A |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)UC-72D, (1)PT-14, (1)PT-17, (1)PT-23, (1)PT-27 Navy(1922-1962): (1)JW, (1)N2S-1/3/4, (1)N2T |
| R-680 | Lycoming R-680-A |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)AT-8, (2)AT-9, (2)AT-10, (1)AT-19, (1)XBQ-2A, (1)UC-72C,
(1)C-81, (3)C-91,
(1)L-1, (1)L-12, (1)O-49(L-1), (1)YPT-9B, (1)YPT-10C, (1)PT-11C/D, (1)PT-13,
(1)T-31 Navy(1922-1962): (1)NP, (1)NQ, (1)N2S-2/5, (1)N4Y, (1)R3Q |
| R-720 | Kinner C-5 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)YPT-9C, (1)YPT-10D, (1)PT-11B |
| R-755 | Jacobs L-4 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)AT-17, (1)UC-43J, (1)UC-72K, (2)C-78, (1)C-126, (1)G-1, (1)PT-18,
(1)R-3 Navy(1922-1962): (2)JRC |
| R-760 | Wright Whirlwind 7 (J-6) |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)UC-70C, (1)UC-72B/F, (1)UC-77A, (1)UC-81B/G/H/J, (1)C-88, (1)PT-15 Navy(1922-1962): (1)JK, (1)J2W, (1)N2C, (1)N3N, (1)N5N, (1)NY-3, (1)OO |
| R-790 | Wright Whirlwind 9 (J-5) |
Army(1919-1924): (1)NO-2 Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)AT-5, (3)C-2, (3)C-3, (1)O-14, (1)O-15, (1)O-17, (1)PT-2, (1)PT-3 Navy(1922-1962): (1)NK, (1)NS, (1)NY, (1)N3Y, (2)XPS-1, (3)TA(RA), (3)RA |
| R-830 | Jacobs L-5 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)UC-43D/G, (1)UC-70D, (1)UC-72E/H/M/N |
| R-915 | Jacobs L-6 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)AT-20, (1)UC-43C, (1)UC-70A/B, (1)UC-72A/G/J/L/P, (1)O-60, [(1)O-61], (1)R-2 |
| R-975 | Wright Whirlwind 9 (J-6) |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)BT-3, (1)BT-6, (1)BT-9, (1)BT-15, (2)BQ-6, (3)C-7, (3)C-9,
(2)C-21, (2)UC-36C, (1)UC-43A/E/F/H/K, (1)UC-77, (1)G-2, (1)H-25, (2)OA-3,
(1)V-1 Navy(1922-1962): (1)F9C, (1)HJP(HUP), (1)HJS, (1)HUP, (1)JB, (2)RC, (2)RD, (1)R3O, (1)SNC, (2)TD3R |
| DR-980 | Packard DR-980 Diesel | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)PT-8 |
| R-985 | Pratt & Whitney Wasp Junior |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)AT-7, (2)AT-11, (1)BT-5, (1)BT-7, (1)BT-8, [(1)BT-11], (1)BT-12,
(1)BT-13, (1)BT-14, (1)BT-16, (1)BT-17, (2)C-26, (1)C-28, (2)C-36, (2)C-37,
(2)C-40, (1)C-43, (2)C-45, (1)UC-61D, (1)C-70, (1)UC-71, (1)UC-72, (1)UC-81D/E/F,
(2)F-2, (1)L-12A, (1)L-20(U-6), (1)O-51, (2)OA-4, (2)OA-9, (2)OA-13, (1)P-21,
(1)PT-12, [(1)PQ-11], (1)R-1, (1)R/H-5, (2)R-10, (1)V-3 Navy(1922-1962): (1)GB, (1)GH, (2)HJH, (1)HO2S, (1)HO3S, (2)J3F(JRF), (2)JO, (1)JQ(RQ), (2)JRB(C-45), (2)JRF, (1)NH, (1)OJ, (1)OK, (1)OS2N, (1)OS2U, (2)R2O, (1)RQ, (2)SNB, (1)SNV Joint(1962+): (1)U-6 |
| R-1044 | Kinner C-7 | Navy(1922-1962): (1)RK |
| R-1300 | Wright/Lycoming |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)H-19, (1)T-28A, [(1)T-30] Navy(1922-1962): (1)HO4S-3(H-19), (1)HRS-3(H-19), (2)ZPG |
| R-1340 | Pratt & Whitney Wasp |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)A-4, (1)AT-6/T-6, (2)AT-13, (2)AT-15, (1)AT-16, (1)BC-1,
(1)BC-2, (1)BC-3, (1)BT-2, (1)BT-10, (3)C-4, (3)C-5, (2)C-6, (1)C-8,
(1)C-12, (1)C-17, (1)C-19, (1)C-23, (1)C-25, (2)C-29, (2)C-35, (2)UC-36B,
(1)C-64, (2)C-73, (1)C-85, (1)C-96, (1)C-101, (2)C-106, (1)F-1,
(1)R/H-12, (1)H-19A/C, (1)H-43C/D,
(1)L-11,
(2)LB-3, (1)O-12, (1)O-19, (1)O-22, [(1)O-24], (1)O-28, (1)O-32, [(1)O-37],
(1)O-52, [(2)OA-7], (1)P-3, (1)P-12, (1)XP-13A, (1)P-15, (1)P-26, (1)P-27,
(1)P-28, (1)P-29 Navy(1922-1962): (1)FA, (1)FB-6/7, (1)F2B, (1)F3B, (1)F4B, (1)F5B, (1)F7B, (1)F6C-4, (1)F7C, (1)F8C, (1)FG, (1)F2G, (1)FH, (1)FJ, (1)F2U, (1)F3W, (1)HOK(H-43), (1)HO4S-1, (1)HRP, (1)HRS-1, (1)HUK(H-43), (1)JA, (1)JE, (1)J2Q(R2Q), (3)JR-3(RR), (1)NJ, (1)OC, (1)O2C, (1)O3C, (1)OL-8/9, (1)O2L, (1)O2N(OSN), (1)O2U, (1)O3U, (1)O4U, (1)O5U, (1)OSN, (1)OSS, (1)OSU, (2)PJ, (2)P3M-1, (2)PS(RS), (2)P2S, (2)PY, (2)RD-3/4, (1)RE, (1)R2Q, (3)RR-3/4/5, (2)RS, (1)SS, (1)SNJ, (1)SOC, (1)SO2C, (1)SON, (1)UC(U-1), (2)ZSG, (2)ZS2G Joint(1962+): (1)U-1 |
| R-1454 | Curtiss | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)O-8, (1)XP-3 |
| R-1510 | Wright Whirlwind 14 | Navy(1922-1962): (1)F11C-1, (1)F12C, (1)F13C, (1)F2J, (1)F3J, (1)FT, (1)S2C, (1)S4C, (1)SBC-2 |
| R-1535 | Pratt & Whitney Twin Wasp Junior |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)A-17, (1)O-46, [(1)P-32] Navy(1922-1962): (1)BG, (1)B2G, (1)BT, (1)B2Y, (1)BFB, (1)F6B(BFB), (1)FD, (1)F2F, (1)F3F-1, (1)F3U, (1)XO3U-5, (1)XSF-2, (1)SBC-3, (1)SBU, (1)SB2U, (1)SB3U |
| H-1640 (note 1) | Curtiss Chieftain |
Army/AF(1924-1962): [(1)A-6], (1)O-18, (1)O-21, (1)P-11, (1)P-13, [(1)P-14] Navy(1922-1962): (1)XOC-3 |
| R-1670 | Wright | Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)A-14, [(1)O-48] |
| R-1690 | Pratt & Whitney Hornet A |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)A-10, (2)B-3, (2)B-12, (1)C-14B, (2)C-56A/C/D, (2)C-59, (1)C-89,
(2)LB-2, [(2)LB-4], (2)LB-7, (2)LB-10, (2)LB-13, (1)O-20, (1)O-38, (2)OA-8,
(2)OA-11 Navy(1922-1962): (1)BM, (1)F6C-5, (2)JRS, (1)O3U-2/4(SU), (2)P3M-2, (2)R5O-2, (1)SU, (1)TG-1, (1)XT3M-3, (1)T4M, (1)T5M |
| R-1750 | Wright Cyclone 9 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)B-5, (1)C-14, (1)C-15, (2)LB-6, (2)LB-9, (2)LB-11, (1)XO-21A,
(1)O-29 Navy(1922-1962): (2)PD, (1)XPH-1, (2)PM-1, (2)PN-11/12, (2)P4N, (2)T2D, (1)XT3M-4, (2)TN, (1)T2N |
| R-1820 | Wright Cyclone 9 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)A-12, (1)A-13, [(2)A-15], (2)A-18, (1)A-24, (1)A-27, (2)A-29,
(1)A-33, (2)AT-18, (2)B-6, (2)B-10, [(2)B-11], (4)B-17, (2)B-18, (4)B-40,
(1)C-11A, (1)Y1C-14A, (1)C-15A, (1)C-22, (1)C-24, (1)C-27B/C, (2)C-30, (1)C-31,
(2)C-32, (2)C-33, (2)C-34, (2)C-38, (2)C-39, (2)C-42, (2)C-49, (2)C-50,
(2)C-51, (4)XC-54K, (2)C-56, (2)C-58, (2)C-60, [(2)C-63], (2)C-68, (4)C-75,
(2)C-84, (1)C-100, (1)C-103, (4)C-108, (2)C-110, (2)C-111, (2)C-117D, (2)C-122C,
(3)C-125, (4)F-9, (1)H-21, (1)H-34,
(1)O-29A, (1)O-38D, (1)O-40, (2)O-44, (2)O-45, (1)O-47, (2)OA-5,
[(2)OA-6], (1)OA-12, (1)P-20, (1)P-36G, (2)P-50, (1)P-64, (2)SA-16(U-16),
(1)T-28 Navy(1922-1962): (1)BT-2, (1)BY, (1)BFC, (1)BF2C, (1)F2A, (1)F8C-7/8, (1)F10C, (1)F11C, (1)FF, (1)F3F-2/3, (1)F4F-5, (1)F5F, (1)FM-2, [(1)F2M], (1)FN, (1)FR, [(1)HRS-4], (1)HSS-1(H-34), (1)HUS(H-34), (1)JF, (1)J2F, (1)JL, (2)JR2F(UF), (1)O2C-2, (4)PB, (2)P2D, (1)PH, (2)PK, (2)PM-2, (3)P2M, (2)P2Y, (2)PBO, (2)R4C, (2)R2D, (2)R3D, (2)R4D-8(C-117), (1)RO, (2)R5O, (1)RT, (1)SC, (1)S3C, (1)SF, (2)S2F(S-2), (1)SBA, (1)SBC-1/4, (1)SBD, (1)SBN, (1)SN2J, (1)SOE, (2)TF(C-1), (1)TG-2, (2)UF(U-16), (2)WF(E-1) Joint(1962+): (2)C-1, (2)E-1, (2)S-2, (2)U-16 |
| R-1830 | Pratt & Whitney Twin Wasp |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)A-16, (1)A-19, (2)A-22, (2)A-28, (1)AT-12, (4)AT-22, (2)B-14,
(4)B-15, (4)B-24, (4)B-41, (2)C-41, (2)C-47, (2)C-48, (2)C-52, (2)C-53,
(2)C-57, [(2)C-62], (2)C-66, (2)C-76, (4)C-87, [(2)C-93], [(2)C-104], (4)C-105,
(4)C-109, (2)C-117, (4)F-7, (2)OA-10, [(1)P-33], [(1)P-34], (1)P-35, (1)P-36,
(1)P-41, (1)P-42, (1)P-43, (1)P-66 Navy(1922-1962): (1)F4F, (1)FM-1, (1)JF-1, (4)JR2S, (2)P3D, (2)P3Y, (2)PB2B, (2)PBN, (4)PBS, (2)PBV, (2)PBY, (4)PB2Y, (4)PB4Y(P4Y,P-4), (2)RB, (2)R4D(C-47), (2)R5O-3, (4)RY, (4)R2Y, (1)XT3D-2, (1)TBD, (1)TBG Joint(1962+): (4)P-4 |
| R-1860 | Pratt & Whitney Hornet B |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)B-4, (2)B-9, [(2)B-13], (1)C-11, (1)C-16, (1)C-18, (4)C-20,
(1)C-27, (2)LB-8, (2)LB-12, (2)LB-14 Navy(1922-1962): (1)XT3D-1, (1)T6M |
| R-2000 | Pratt & Whitney Twin Wasp |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (4)C-54, (2)C-122 Navy(1922-1962): (2)F5U, (4)R5D(C-54) Army(1955-1962): (2)AC-1(CV-2) Joint(1962+): (2)C-7, (2)CV-2(C-7) |
| R-2160 | Wright Tornado | Army/AF(1924-1962): [(1)P-69] |
| R-2180 | Pratt & Whitney Twin Hornet | Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)A-21, [(4)B-20], (2)B-21, (2)H-16, [(1)P-44] |
| R-2600 | Wright Cyclone 14 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)A-20, (1)A-25, (2)A-30, (1)A-31, [(1)A-34], (1)A-35, (2)AT-24,
[(2)B-22], (2)B-23, (2)B-25, [(4)B-33], (2)B-37, (2)C-55, (2)C-67, (4)C-98,
(2)F-3, (2)F-10, [(2)O-53], [(2)O-56], [(2)P-65], (2)P-70 Navy(1922-1962): (2)BD, (1)F6F-1, (2)PBJ, (2)PBM, (4)PB2Y-4, (1)SB2A, (1)SB2C, (1)SBF, (1)SBW, (1)TBF, (1)TBM |
| R-2800 | Pratt & Whitney Double Wasp |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)XA-19B, (2)A-26, (1)A-32, [(2)A-37], [(1)A-39], (2)AT-23, (2)B-26,
[(2)B-27], (2)B-28, (2)B-34, (2)C-46, (2)C-82, (4)C-112, (4)C-118, (2)C-123,
(2)C-131, (2)F-15, (2)H-37,
(1)P-47, (1)P-56, [(2)XP-59(not the jet!)], (1)P-60A/C/E, (2)P-61, (2)T-29, [(2)T-32],
[(2)T-36] Navy(1922-1962): (1)AF, (2)AJ(A-2), (1)AU, (1)BTK, (1)F3A, (1)F15C, (1)F6F, (2)F7F, (1)F8F, (1)FG, (1)F3M, (2)F2T, (1)F4U, (2)HR2S(H-37), (1)HSL, (2)JD, (2)JM, (2)PV, (2)PBM-5, [(4)PB3Y], (2)RM(C-3), (2)R5C(C-46), (4)R6D(C-118), (2)R4Y, [(2)TB2F], (1)TB3F, (1)TBU, (1)TBY Joint(1962+): (2)A-2, (2)C-3 |
| R-3350 | Wright Cyclone 18 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): [(2)A-23], (1)A-31C, (2)A-38, [(1)A-40], (4)B-19, (4)B-29, [(4)B-30],
[(4)B-31], (4)B-32, (2)B-69, (2)XC-46L, (4)C-69, (4)XC-97, (2)C-119, (4)C-121,
(2)C-128, (2)C-134, (4)F-13, (1)P-62 Navy(1922-1962): (1)AD(A-1), (1)BT2C, (1)BTD, (1)BT2D(AD), (1)F14C-2, (4)JRM, (4)P2B, (2)P5M(P-5), (4)PO(WV), (2)P2V(P-2), (2)P4Y, (2)PBB, [(2)PBM-4], (4)PB2M, (4)R7O(R7V), (2)R4Q-2(C-119), [(1)SB3C], (1)SB2D(BTD), (4)R7V(C-121), (4)WV(C-121) Joint(1962+): (1)A-1, (2)P-2, (2)P-5 |
| R-4090 | Wright 792C22AA | |
| R-4360 | Pratt & Whitney Wasp Major |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)XA-31B, [(1)A-41], (4)B-35, (6)B-36, (4)B-44, (4)B-50, (4)C-74,
(4)C-97, (6)C-99, (2)C-119A/B/C, (2)C-120, (4)C-124, (2)F-11, (4)F-12(R-12),
[(2)P-71], (1)P-72 Navy(1922-1962): (1)AM, (1)BTC, (1)BTM(AM), (1)F8B, (4)JRM-2, (2)P4M, (4)R6O(R6V), (2)R4Q-1(C-119), (4)R6V, (1)TB2D |
| R-7755 | Lycoming XR-7755 |
| V-720 | Wright | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)AT-1, [(1)AT-2], (1)AT-3, (1)AT-4, (1)PT-1 |
| V-770 | Ranger SGV-770B-3 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)AT-14, (2)AT-21, (2)BQ-3, (1)O-50, (1)P-77 Navy(1922-1962): (1)F6C-7, (1)OSE, (1)SO3C, (1)SO2U, (1)TE |
| V-1150 | Curtiss D-12 |
Army(1919-1924): (1)PW-7, (1)PW-8, (1)PW-9, (1)R-6, (1)R-8 Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)A-3, (1)BT-4, (1)O-1, (1)P-1, (1)P-5 Navy(1922-1962): (1)F6C-1/2/3/6, (1)MO, (1)M2O, (1)NO, (1)R2C |
| V-1400 | Curtiss |
Army(1919-1924): (1)NO-1 Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)P-2 Navy(1922-1962): (1)R3C |
| V-1410 | Allison-Liberty IV-1410 Liberty |
Army(1919-1924): (1)CO-6, (1)XCO-7B Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)A-2 |
| V-1440 | Continental | |
| V-1460 | Wright IV-1460 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)O-10, (1)XOA-1A, (1)OA-2, (1)P-17 |
| V-1510 | Curtiss | |
| V-1560 | Wright IV-1560 | Army/AF(1924-1962): [(1)P-18], [(1)P-19] |
| V-1570 | Curtiss Conqueror |
Army/AF(1924-1962): [(1)A-5], (1)A-7, (1)A-8, [(1)A-9], (1)A-11, (2)B-1, (2)B-2,
(2)B-7, (2)B-8, (2)Y1B-9, (1)O-13, (1)O-16, (1)O-23, (1)O-25, (1)O-26,
(2)O-27, [(2)O-30], (1)O-31, (1)O-33, (1)O-34, (2)O-35, (2)O-36, (1)O-39,
[(1)O-41], (1)O-43, (1)P-6, (1)P-7, (1)P-9, (1)P-10, (1)P-16(PB-1), (1)P-22,
(1)P-23, (1)P-24, (1)P-25, (1)P-30(PB-2), (1)P-31, (1)PB-1, (1)PB-2 Navy(1922-1962): (4)P2H |
| V-1650 | Liberty Liberty 12 |
Army(1919-1924): (1)A-1, (1)A-2, (1)CO-1, (1)CO-2, (1)CO-3, (1)CO-4, (1)CO-5,
(1)CO-7, (1)CO-8, (2)GA-1, (1)IL-1, (6)NBL-1, (2)NBS-1, (2)NBS-2, (2)NBS-3,
(2)NBS-4, (2)T-1, (1)T-2, (1)T-3 Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)BT-1, (1)C-1, (2)LB-5, (1)O-1A, (1)O-2, [(1)O-4], (1)O-5, (1)O-6, (1)O-11, (1)OA-1 Navy(1922-1962): (1)O2B, (1)OL-4 |
| V-1650 | Packard/Rolls-Royce Merlin | Army/AF(1924-1962): (4)C-115, (1)F-6, (1)P-40F/L, (1)P-51, (1)XP-60/D, [(1)XP-63B], [(1)P-78], (2)P/F-82/B/C/D/E |
| V-1710 | Allison |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)XA-11A, (1)A-36, (2)A-42, [(6)B-16], (4)B-38, (2)B-42, (4)C-114,
(4)C-116, (2)F-4, (2)F-5, (1)F-6A, (2)FM-1, (1)P-37, (2)P-38, (1)P-39,
(1)P-40, (1)P-45, (1)P-46, [(1)XP-47/A], (1)P-51/A/J, (1)P-55, (1)XP-60A/B, (1)P-63,
[(1)P-76], (2)P/F-82A/F/G/H Navy(1922-1962): (1)FL, (1)FO |
| V-1950 | Wright T-3 | Army/AF(1924-1962): [(1)O-3] |
| V-3420 | Allison | Army/AF(1924-1962): (4)B-39, (2)P-58, (1)P-75 |
Notes:
1. The Curtiss Chieftain engine was of a unique configuration, and was originally classed as a "hexagonal" engine - hence the "H" prefix. It was later redesignated as the R-1640 radial engine.
3 Jet and Turbine Engines, 1946 - 1968
After World War II, the Army and the Navy defined a system for designating gas turbine and other jet engines. The system was formally laid down in Air Force/Navy Aeronautical (ANA) Bulletin 306. This ANA Bulletin was updated several times, the final edition being ANA Bulletin 306M, dated 27 December 1963. On 1 May 1968, a revised system was defined by MIL-STD-879. The latter was finally absorbed into the current standard MIL-STD-1812 on 28 February 1991.
| Examples: | Y | T | 56 | - | A | - | 1 | |
| J | 35 | - | A | - | 21 | C | ||
| (6) | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
The one- or two-letter code (1) designates the type of the engine:
- J - Turbojet
- T - Turboprop or Turboshaft
- PJ - Pulsejet
- RJ - Ramjet
- TF - Turbofan (added in 1959)
(2) is the model number of the engine. Note that there is no dash between the engine type letter and the model number. The Army and Air Force used odd numbers from 31 up, while the Navy used even numbers from 30 up. Why each numerical sequence was started at 30, I don't know. The numbers were assigned in numerical sequence separately by each service, so the Navy-sponsored J52 was in fact a later engine than the J65, because Navy J-numbers "lagged behind" the Army/AF ones.
(3) is a one- or two-letter code for the manufacturer of the engine. The following is a list of all assigned code letters, not all of which were actually used for jet engines:
- A - Allison Div. (General Motors)
- AC - Allis-Chalmers Manufacturing Co.
- AH - American Helicopter Div. (Fairchild)
- AJ - Aerojet General Corp.
- AM - Aeromarine Co.
- AN - Aeronutronics Corp.
- B - Buick Motor Div. (General Motors)
- BA - Bell Aircraft Corp.
- BL - Bridgeport-Lycoming Div. (AVCO)
- BO - Boeing Co.
- C - Chevrolet Div. (General Motors)
- CW - Curtiss-Wright Propeller Div.
- D - Chrysler Corp.
- DL - De Laval Steam Turbine Co.
- E - Aircooled Motors, Inc. (Franklin)
- EE - Elliot Manufacturing Co.
- F - Ford Motor Co.
- FF - Frederic Flader, Inc.
- G - Warner Aircraft Corp.
- G - Garrett Corp., AiResearch Div.
- GE - General Electric, Gas Turbine Div.
- GN - G.M. Giannini & Co, Inc.
- H - Hiller Helicopters
- HM - Harvey Machine Co., Inc.
- J - Jacobs Aircraft Engine Co.
- JH - Joshua Hendy Iron Works (to "NH" later)
- K - M.W. Kellogg, Inc.
- KA - Kiekhafer-Aeromarine Motors, Inc.
- KF - Kaiser-Frazer Engine Div.
- KM - Kaiser Manufacturing
- L - Lycoming Div. (AVCO)
- LA - Lockheed Aircraft Corp.
- MA - Marquardt Aircraft Co.
- MD - McDonnell Aircraft Corp.
- MH - McCulloch Motors Corp.
- MN - Menasco Manufacturing Co.
- NA - North Amrican Aviation, Inc.
- NH - Northrop Aircraft, Inc. (formerly Hendy)
- NK - Nash-Kelvinator Corp.
- OEL - Orenda Engines (Hawker Siddeley Canada)
- P - Pratt & Whitney
- PM - Packard Motor Car Co. (was "V")
- R - Fairchild Engine Div.
- RM - Reaction Motors, Inc.
- RP - Radioplane Div. (Northrop)
- RR - Rolls-Royce, Ltd.
- S - Solar Aircraft Co.
- ST - Studebaker Corp.
- T - Continental Motors Corp.
- TT - Taylor Turbine (Rolls-Royce agent)
- V - Packard Motor Car Co. (to "PM")
- W - Wright Aeronautical Corp.
- WE - Westinghouse Electric Corp.
- WS - West Engineering Co.
The same code letters were used in serial numbers for all types of engines, including piston and rocket engines. This explains why code letters were also assigned to companies which never developed or manufactured jet or turbine engines.
The number (4) designates a specific model of the engine. The Army and Air Force use odd numbers from 1 up, while the Navy uses even numbers from 2 up.
(5) is an optional letter for designating minor modifications of an engine model. Letters are assigned alphabetically from A on (I and O are not used). The letter W is reserved for engines with water injection, while the combination "WA" is used for engines with water-alcohol injection.
(6) is an optional status prefix:
- X - Experimental
- Y - Service Test
- Z - Obsolete
Designation List:
| Designation | Manufacturer and Model | Remarks; Aircraft |
|---|---|---|
| J30 | Westinghouse 19XB |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)XP-79B, [(1)XF-92], (2)X-4 Navy(1922-1962): (2)FH |
| J31 | General Electric I-16 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)P-59 Navy(1922-1962): (1)FR, (1)F2R |
| J32 | Westinghouse 9.5A/B | Navy(1922-1962): (1)KDN |
| J33 | General Electric/Allison I-40 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)P/F-80, (1)P-81, (2)P-83, (1)XF-92A, (1)F-94A/B, (1)T-33 Navy(1922-1962): (1)AJ(A-2), (1)F9F-3/4, (2)P4M, (1)TO(TV), (1)TV(T-33), (1)T2V(T-1) Joint(1962+): (1)A-2, (1)T-1 Missiles: (1)TM-61(MGM-1), (1)TM-76(CGM-13), (1)SSM-N-8(RGM-6) |
| J34 | Westinghouse 24C |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)B-69, (1)P/F-85, (4)P/F-87, (2)F-88, (2)F-90, (2)X-3, (1)X-18 Navy(1922-1962): (2)F3D(F-10), (2)F2H(F-2), (1)FR-4, (1)F6U, (2)F7U-1/2, (1)XF2Y-1, (2)P2V-5F/6F/7(P-2), (1)T2J-1(T-2) Joint(1962+): (1)F-2, (2)F-10, (2)P-2E/G/H/J, (1)T-2A Other: (1)Douglas D-558-2 |
| J35 | General Electric/Allison TG-180 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)B-43, (4)XB-45, (4)B-46, (4)B-48, (8)B-49, (2)H-17,
(1)P/F-84, (1)XP-86, (2)F-89, (1)F-96, (2)X-5 Navy(1922-1962): (1)FJ-1 Other: (1)Douglas D-558-1 |
| J36 | Allis-Chalmers (DeHavilland Goblin) | Navy(1922-1962): (1)F15C |
| J37 | Lockheed L-1000 | |
| J38 | West Engineering | |
| J39 | General Electric I-20 | (similar to J31; cancelled) |
| J40 | Westinghouse 40E |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)X-10 Navy(1922-1962): (2)XA3D-1, (1)XF4D-1, (1)F10F, (1)F3H-1 |
| J41 | Packard PT-104/PT-4000 | (cancelled project) |
| J42 | Pratt & Whitney (Rolls-Royce Nene) | Navy(1922-1962): (1)F9F-2 |
| J43 | Westinghouse | (became XJ30-WE-8) |
| J44 | Fairchild |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)C-123J, (1)Q-1, (1)Q-3 Navy(1922-1962): (1)KDA-1 |
| J45 | Westinghouse | (became XJ34-WE-4) |
| J46 | Westinghouse 24C | Navy(1922-1962): (2)F7U-3, (2)YF2Y-1 |
| J47 | General Electric TG-190 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (4)B-36D/E/F/H/J, (4)B-45, (6)B-47, (2)KB-50J/K, (3)B-51, (2)KC-97L,
(1)F-86, (1)F-91, (1)F-95(F-86D) Navy(1922-1962): (1)FJ-2 |
| J48 | Pratt & Whitney JT7 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)F-93, (1)F-94C, (1)F-97(F-94C) Navy(1922-1962): (1)F9F-5/6/7/8(F-9) Joint(1962+): (1)F-9 |
| J49 | Packard PT-205 | (cancelled project) |
| J50 | Westinghouse | |
| J51 | Wright TJA-1 | (cancelled project) |
| J52 | Pratt & Whitney JT8 |
Navy(1922-1962): (1)A4D(A-4), (2)A2F(A-6) Joint(1962+): (1)A-4, (2)A-6 Missiles: (1)GAM-77(AGM-28) |
| J53 | General Electric | Army/AF(1924-1962): [(4)X-6] |
| J54 | Westinghouse (Rolls-Royce Avon) | |
| J55 | Flader 124 | Army/AF(1924-1962): [(1)Q-2] |
| J56 | Allison | |
| J57 | Pratt & Whitney JT3 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (8)B-52, (2)RB-57D, (8)B-60, (4)C-135A, (1)F-100, (2)F-101,
(1)F-102, [(2)X-16] Navy(1922-1962): (2)A3D(A-3), (1)F4D(F-6), (1)F5D, (1)F8U(F-8) Joint(1962+): (2)A-3, (1)F-6, (1)F-8, (1)U-2A/B/E Missiles: (1)SM-62 |
| J58 | Pratt & Whitney JT11D | Joint(1962+): (2)F-12, (2)SR-71 |
| J59 | Wright TJ-7 | (cancelled project) |
| J60 | Pratt & Whitney JT12 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)RB-57F, (4)C-140, (2)T-39, [(2)T-40] Navy(1922-1962): (2)T2J-2(T-2), (2)T3J(T-39) Army(1955-1962): (2)VZ-10(V-4) Joint(1962+): (2)H-59, (2)T-2B, (2)XV-4A |
| J61 | Wright TJ-6 | (cancelled project) |
| J62 up (even) | Most probably not assigned | |
| J63 | Fairchild | |
| J65 | Wright (Armstrong-Siddeley Sapphire) |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)B-57, (1)F-84F, (1)XF-104 Navy(1922-1962): (1)A4D-1/2(A-4), (1)FJ-3/4(F-1), (1)F11F(F-11) Joint(1962+): (1)A-4A/B/C/L/P/Q, (1)F-1, (1)F-11 |
| J67 | Wright (Bristol Olympus) | Army/AF(1924-1962): [(4)B-59], [(1)F-103] |
| J69 | Continental 352 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)Q-1A/B, (2)T-37 Navy(1922-1962): (2)TT Army(1955-1962): (3)VZ-9 Joint(1962+): (2)A-37A Missiles: (1)GAM-67, (1)AQM/BQM-34, (1)AQM-103 |
| J71 | Allison |
Army/AF(1924-1962): [(4)B-56], (2)B-66, (2)YF-89E Navy(1922-1962): (1)F3H(F-3), (4)P6M-1 Joint(1962+): (1)F-3 |
| J73 | General Electric |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)F-86H Navy(1922-1962): [(1)F3H-3] |
| J75 | Pratt & Whitney JT4 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)F-105, (1)F-106, (1)F-107 Navy(1922-1962): (1)F8U-3, [(2)F2Y-2], (4)P6M-2 Joint(1962+): (1)TR-1, (1)U-2C/D/F/G/H/R |
| J77 | General Electric | |
| J79 | General Electric X-24A |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (4)B-58, (1)F-104, (2)F-110(F-4), (2)X-21 Navy(1922-1962): (2)A3J(A-5), (2)F4H(F-4), (1)F11F-1F Joint(1962+): (2)A-5, (2)F-4, (1)F-21 Missiles: (1)SSM-N-9(RGM-15) |
| J81 | Westinghouse (Rolls-Royce Soar) |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)Q-4(AQM-35) Missiles: (1)AQM-35 |
| J83 | Fairchild | Missiles: (1)SM-73 |
| J85 | General Electric CJ610 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)C-119K, (2)C-123K, (1)Q-4B(AQM-35B), (2)T-38, (2)X-14 Army(1955-1962): (2)VZ-11(V-5) Joint(1962+): (2)A-37B, (2)F-5, (2)T-2C/D/E, (6)XV-4B, (2)V-5 Missiles: (1)GAM-72(ADM-20), (1)AQM-35B, (1)MQM-34D Other: (2)Lockheed "HAVE BLUE" |
| J87 | General Electric X-211 | (nuclear powered engine; cancelled) |
| J89 | Allison | (low-bypass turbofan engine; unsuccessful competitor to J93 for use in B-70) |
| J91 | Pratt & Whitney JTN9 | (higher-bypass turbofan engine; unsuccessful competitor to J93 for use in B-70; also considered as a nuclear engine) |
| J93 | General Electric 7E | Army/AF(1924-1962): (6)B-70, [(2)F-108] |
| LJ95 (note 1) | Teledyne CAE 365 | |
| J97 | General Electric GE1 | Missiles: (1)AQM-91, (1)GQM-94 |
| J99 | Rolls-Royce | Other: Grumman 754 RPV |
| T30 | Westinghouse | |
| T31 | General Electric TG-100 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)C-113, (1)P-81 Navy(1922-1962): (1)F2R |
| T32 | Pratt & Whitney | |
| T33 | Flader Brigadier | (cancelled project) |
| T34 | Pratt & Whitney PT2 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (4)YC-97J, (4)YC-121F, (4)YC-124B, (4)C-133 Navy(1922-1962): (4)R7V-2(C-121) |
| T35 | Wright | (cancelled project) |
| T36 | Chrysler | |
| T37 | Northrop Turbodyne | Army/AF(1924-1962): [(4)EB-35B] |
| T38 | Allison 501F-1 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)F-88B, (2)H-27(YH-16A), [(2)T-29E] |
| T39 | Allison 504 | (cancelled project) |
| T40 | Allison 500 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)XF-84H, (2)X-18 Navy(1922-1962): (1)A2D, (2)A2J, (1)FV, (1)FY, [(2)P3B], (4)P5Y, (4)R3Y |
| T41 | General Electric TG-110 | (derivative of T31; project cancelled) |
| T42 | De Laval | |
| T43 | Wright GTC-1 | (cancelled project) |
| T44 | Allison 503 | (cancelled project; similar to T40, but with 3 instead of 2 power sections) |
| T45 | Pratt & Whitney PT4 | (cancelled project) |
| T46 | Fairchild | |
| T47 | Wright | |
| T48 | Pratt & Whitney | |
| T49 | Wright TP51A2 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)XB-47D |
| T50 | Boeing 502-2E | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)XL-19B, (1)QH-50 |
| T51 | Continental 220 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)XH-13F, (1)H-39, (1)XL-19C |
| T52 | Pratt & Whitney | |
| T53 | Lycoming LTC1 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)H-40, (1)H-43 Navy(1922-1962): (2)OF(OV-1) Army(1955-1962): (1)VZ-2, (1)VZ-3 (1)VZ-4 Joint(1962+): (1)H-1, (2)OV-1 |
| T54 | Allison | (Twin T56) Navy(1922-1962): [(1)XFV-2] |
| T55 | Lycoming LTC4/AL55 | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)YAT-28E, (2)H-47, (2)X-19 |
| T56 | Allison 501D |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (4)C-130, (2)C-131C/H, (2)YH-16B Navy(1922-1962): [(2)HRH], (2)W2F(E-2), (4)P3V(P-3) Joint(1962+): (2)C-2, (2)E-2, (4)P-3 |
| T57 | Pratt & Whitney PT5 | Army/AF(1924-1962): [(4)C-132] |
| T58 | General Electric CT58 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)H-21D, (2)SH-34H, (2)H-46, (1)H-48 Navy(1922-1962): (2)HRB(H-46), (2)HSS-2(H-3), (1)HU2K(H-2), (1)HU2S(H-52) Army(1955-1962): (1)VZ-5 Joint(1962+): (1)UH-1F/P, (1)UH-2A/B, (2)H-2, (2)H-3, (1)H-52, (4)X-22 |
| (T59) | (No information) | |
| T60 | Boeing | |
| T61 | Allison | |
| T62 | Solar Mercury | |
| T63 | Allison 250 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)UH-13R Navy(1922-1962): (1)HUL-1M Joint(1962+): (1)H-4, (1)H-6, (1)H-57, (1)H-58, (1)H-67, (1)V-11 |
| T64 | General Electric |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (4)C-142 Joint(1962+): (2)C-27, (2)H-53, (3)H-53E, (1)H-56, (2)V-9 |
| T65 | Continental TS325-1 | |
| T66 | Solar | |
| T67 | Continental 217A-2A | |
| T68 | Rolls-Royce | |
| T69 | Continental | |
| T70 | Westinghouse | |
| T71 | Allison | |
| T72 | Continental | |
| T73 | Pratt & Whitney JFTD12 | Joint(1962+): (2)H-54 |
| T74 | Pratt & Whitney PT6 | Joint(1962+): (2)U-21E/G (see note 2) |
| T75 up (odd) | Most probably not assigned | |
| T76 | Garrett-AiResearch TPE331 | Joint(1962+): (2)C-26, (1)U-23, (2)OV-10 |
| T78 | Allison 545 | (development only, not flown) |
| T80 | Allison | (cancelled project) |
| (PJ30) | (No information) | |
| PJ31 | Ford |
Army(1924-1962): (1)JB-2(LTV-A-1), (1)JB-4, (1)JB-10 Navy(1922-1962): (1)KGW(KUW,LTV-N-2) Missiles: (1)LTV-A-1, (1)LTV-N-2 |
| PJ32 | Solar | Navy(1922-1962): (1)KD2G |
| PJ33 | Giannini | |
| (PJ34) | (No information) | |
| PJ35 | Giannini | |
| (PJ36) | (No information) | |
| PJ37 | Giannini | |
| (PJ38) | (No information) | |
| PJ39 | Giannini | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)XQ-1 |
| PJ40 | Marquardt | |
| (PJ41) | (No information) | |
| PJ42 | McDonnell | |
| (PJ43) | (No information) | |
| (PJ44) | (No information) | |
| (PJ45) | (No information) | |
| PJ46 | Marquardt | Navy(1922-1962): (1)KD5G |
| (PJ47) | (No information) | |
| (PJ48) | (No information) | |
| PJ49 | American Helicopter | Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)H-26 |
| RJ30 | Marquardt C-20 | Navy(1922-1962): (1)KDM |
| RJ31 | Marquardt C-30 | |
| (RJ32) | (No information) | |
| (RJ33) | (No information) | |
| RJ34 | Marquardt | |
| RJ35 | Continental | (cancelled project) |
| (RJ36) | (No information) | |
| RJ37 | Menasco A-J-20 | (cancelled project) |
| (RJ38) | (No information) | |
| RJ39 | Marquardt C-48 | |
| RJ40 | Pratt & Whitney | |
| RJ41 | Wright | |
| RJ42 up (even) | Most probably not assigned | |
| RJ43 | Marquardt |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)X-7 Missiles: (1)IM-99 Other: (1)Lockheed D-21 |
| RJ45 | Continental R-20 | (cancelled project) |
| RJ47 | Wright |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)X-7 Missiles: (2)SM-64(Sustainer) |
| RJ49 | Continental | (cancelled project) |
| RJ51 | Wright | |
| (RJ53) | (No information) | |
| RJ55 | Wright | Army/AF(1924-1962): [(1)F-103] |
| RJ57 | Marquardt | |
| RJ59 | Marquardt | Other: [(2)Convair "Kingfish"] |
| TF30 | Pratt & Whitney JTF10A |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (2)F-111 Navy(1922-1962): [(2)F6D] Joint(1962+): (1)A-7, (2)F-14, [(1)X-27] |
| TF31 | General Electric X-84 | (proposed for OXCART (Lockheed A-12); cancelled) |
| TF32 | Allison | (competitor to TF34; cancelled) |
| TF33 | Pratt & Whitney JT3D |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (8)B-52H, (2)RB-57F, (4)C-135, (4)C-137, (4)C-141 Joint(1962+): (4)C-18, (4)C-24, (4)E-3, (4)E-8 |
| TF34 | General Electric CF34 |
Joint(1962+): (2)A-10, (2)S-3 Missiles: [(1)GQM-94B] |
| TF35 | General Electric | (derivative of Model CJ 805-23) |
| TF36 up (even) | Most probably not assigned | |
| TF37 | General Electric CF700 | |
| TF39 | General Electric CTF39 | Joint(1962+): (4)C-5 |
| TF41 | Allison | Joint(1962+): (1)A-7D/E/H/K |
Notes:
1. "LJ" probably means "Lift Jet". I don't know for sure, whether the LJ95 really fits into the J-sequence, but considering the high number (making a separate LJ-series unlikely) and the fact, that J95 would be missing otherwise, I risk a guess.
2. It seems, that only the basic PT6 engine is designated as T74. Many aircraft use the PT6A version, which is
always (exception: T101 for C-23, see below) listed as such in official
military documents and data sheets. Aircraft using the PT6A are:
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)T-34C
Joint(1962+): (2)C-6, (4)RC-7B, (2)C-12, (4)O-5, (1)T-6, (2)T-44, (2)U-21,
(1)U-24, (1)U-27, (2)V-18, (1)V-20
Missiles: (1)GQM-93
4 Rocket Engines
4.1 Liquid Fuel Rockets
The designation system for liquid fueled rockets was originally devised in the 1940's and formally defined in Air Force/Navy Aeronautical (ANA) Bulletin 352 (25 June 1948), later included in MIL-STD-815 (USAF only, 14 June 1962) and finally absorbed into the current standard MIL-STD-1812 (28 February 1991). The system (the familiar "LR" designations) has gone through all this essentially unchanged and is discussed in section 5.2 about current rockets. The only difference in the original 1948 system was, that odd model numbers were reserved for the Air Force and Army, while the Navy used only even model numbers. This is similar to early jet engine designations, except that for liquid rockets, the sequence started at 1 instead of 30.
4.2 Solid Fuel Rockets
The original designation system for solid rockets was completely different from today's system and was defined in Air Force/Navy Aeronautical (ANA) Bulletin 353 (22 July 1948). This designation system was abandoned in the 1960's. The Air Force created a new scheme, very similar to that for liquid rockets, and included it in MIL-STD-815 (14 June 1962). The latter system was finally absorbed into the current standard MIL-STD-1812 and is discussed in section 5.2 about current rockets. After abandoning ANA Bulletin 353, the Navy used its MARK/MOD nomenclature system, while the Army used its Ordnance Number nomenclature.
The original (ANA Bulletin 353) designations for solid rocket motors looked like this:
| Example: | 1.8 | KS | 7800 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) |
The number (1) is the burn time of the motor in seconds.
The two-letter code (2) indicates the type of propellant. The type codes were assigned by the Solid Propellant Information Agency (SPIA).
-
First letter:
- A - Asphalt Perchlorate
- B - Ball or Chopped Double Base Powder
- C - Picrate Nitrate Types
- D - Cast Double Base
- E - Extruded Double Base
- K - Other Perchlorate with Nitrogen Compounds (e.g. Ammonium Perchlorate NH4ClO4)
- N - Other Nitrates and Nitrogen Compounds
- P - Plastic Composition
- S - Solid Composition
Second letter:
Number (3) is the thrust of the motor in pounds.
Note: There are no dashes and blanks between the three elements of the designation.
5 The Current System (MIL-STD-1812A)
On 28 February 1991, MIL-STD-1812 became formally effective. This standard combined several equipment designation systems, which shared common definitions and procedures, into a single document. Included were the type designation systems for all aerospace engines. On 14 February 1997, MIL-STD-1812 was renamed as MIL-HDBK-1812. The change from "Standard" to "Handbook" meant, that the use of the designation systems was no longer mandatory. This "legalized" the long standing practice of using manufacturers' designations for commercial equipment procured "off the shelf". Otherwise, MIL-HDBK-1812 was identical to MIL-STD-1812. However, on 9 October 2020, the document was again renamed to a mandatory "Standard", MIL-STD-1812A. It is essentially identical to MIL-HDBK-1812, but adds the engine type "A".
5.1 Air-Breathing Engines
For turbine engines, the MIL-STD-879 system (now absorbed by MIL-STD-1812) has not changed a lot from the previous system defined in ANA Bulletin 306. The engine type designators and model numbering methods were just revised a little bit. Piston engines, however, are no longer supposed to use the displacement-based designations, but this seems to be a purely theoretical change, because no new piston engines are developed specifically for the military market and new commercial piston engines are operated with their manufacturers' designations. The latter is probably done, because the major American manufacturers of modern piston engines give their engines designations closely following the original "arrangement-displacement" system.
| Examples: | Y | F | 119 | - | PW | - | 100 | |
| T | 700 | - | GE | - | 701 | C | ||
| (6) | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
The letter (1) designates the type of the engine:
- J - Turbojet
- T - Turboprop or Turboshaft
- F - Turbofan
- A - Adaptive Turbofan (added in MIL-STD-1812A)
- O - Piston, Opposed
- R - Piston, Radial
- V - Piston, Vee
- C - Rotating Combustion
- P - Other
I don't know any engine designated in this system with an "O", "R", "V", "C" or "P" designation.
(2) is the model number of the engine. Note that there is no dash between the engine type letter and the model
number. The Air Force uses model numbers 100 to 399, the Navy uses 400 to 699 and the Army uses 700 to 999.
The numbers are assigned in numerical sequence separately by each service.
The T800 designation for the engine of the Army's RAH-66 Comanche is therefore not strictly conforming to the system,
because the Army apparently started a new sequence at 800. Instead, it should have been designated T704
(or whatever the next available number was).
(3) is a two-letter code for the manufacturer of the engine. A few three-letter codes are assigned to non-US manufacturers or joint-venture companies. The following is a list of all assigned code letters (the same letters are used for rocket engine designations), including those which are obsolete now and no longer listed in the latest standard.
- AB - Allegany Ballistics Lab.
- AC - AMOCO Chemicals Corp.
- AD - Allison Div. (General Motors)
- AE - Aerodyne Corp. (formerly AD)
- AI - Astropower, Inc.
- AJ - Aerojet General Corp.
- AN - Aeronutronics Corp.
- AR - Atlantic Research Corp.
- AS - Astrosystems, Inc.
- BA - Bell Aerosystems Co.
- BG - B.F. Goodrich Co. (formerly G)
- CA - Continental Aviation And Engineering Corp.
- CF - CFM International
- CP - United Aircraft of Canada Ltd.
- CW - Curtiss-Wright Corp.
- GA - AiResearch Div. (Garrett Corp.)
- GE - General Electric Co.
- GT - General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc.
- IHI - Ishikawajima Heavy Industries Co., Ltd., Japan
- HP - Hercules Powder Co.
- HT - Hughes Tool Co.
- LHT - Light Helicopter Turbine Engine Co. (LHTEC)
- LD - Lycoming Div. (AVCO)
- LP - Lockheed Propulsion Co.
- MA - Marquardt Corp.
- MAN - Maschinenfabrik Augsburg-Nürnberg, Germany
- MT - Microturbo
- MTU - Motoren- und Turbinen-Union (DaimlerChrysler), Germany
- NA - North American Rockwell Corp. (Rocketdyne)
- NC - Northrop Carolina Corp.
- NM - Naval Missile center
- NP - Naval Propellant Plant No. 5
- NW - Naval Weapons center
- OM - Olin Mathieson Co.
- PA - Picatinny Arsenal
- PW - Pratt & Whitney
- RC - Rocket Research Corp. (formerly RR)
- RD - Rocketdyne (now Rockwell/Hercules)
- RM - Reaction Motors Div. (Thiokol)
- RO - Rotax
- RP - Rocket Power, Inc.
- RR - Rolls Royce Ltd.
- SP - Sunstrand Power Systems
- TC - Thiokol Chemical Corp.
- TR - TRW Systems
- UT - United Technology Center
- WA - Curtiss-Wright Corp. (cancelled, use CW)
- WR - Williams Research Corp.
- WV - United Aircraft of West Virginia
- ZZ - any contractor not listed (also used, if contractor is not yet determined)
Of course, new letters may be assigned, when companies change names, merge or found special joint-venture companies.
The number (4) designates a specific model of the engine. The same method for assignment as for the basic model
numbers applies: The Air Force uses numbers 100 to 399, the Navy uses 400 to 699 and the Army uses 700 to 999.
It is possible, that an Air Force engine, when used by the Navy, gets a Navy model number, e.g. F110-GE-400.
If a new model of an engine designated within the "old" numerical sequence is procured, model suffixes from
the "new" system may be assigned. This results in designations like T64-GE-416A. For the first such assigment,
usually the next available number in the "old" model series is taken and added to the "base block number" of the
relevant service, e.g. T55-L-11 was followed by T55-L-712.
(5) is an optional letter for designating minor modifications of an engine model. Letters are assigned alphabetically from A on (I and O are not used). The letter W is reserved for engines with water injection.
(6) is an optional status prefix:
- X - Experimental
- Y - Service Test
Designation List:
| Designation | Manufacturer and Model | Remarks; Aircraft |
|---|---|---|
| J100 | Teledyne CAE | Missiles: (1)AQM-34P/Q/R |
| J101 | General Electric GE15 | Joint(1962+): (2)F-17 |
| J102 | Allison | (supersonic missile engine) |
| J400 | Williams WR24 |
Joint(1962+): (3)X-48 Missiles: (1)BQM/MQM-74, (1)AGM-154D/E |
| J401 | Garrett AiResearch | |
| J402 | Teledyne CAE 370/372/373 | Missiles: (1)AGM-84, (1)MQM-107, (1)BQM-108, (1)AGM/RGM/UGM-109, (1)AGM-158, (1)AGM-159 |
| J403 | Microturbo TRI 60-3 | Missiles: (1)BQM-126 |
| J700 | Teledyne CAE 312 | Missiles: (1)ADM-141B/C |
| T100 | Sunstrand | |
| T101 | Pratt & Whitney PT6A-45A | Joint(1962+): (2)C-23 |
| T400 | Pratt & Whitney PT6T | Joint(1962+): (1)AH-1J/T, (1)UH-1N/Y, (1)H-59 |
| (T401) | (No information) | |
| (T402) | (No information) | |
| (T403) | (No information) | |
| (T404) | (No information) | |
| T405 | Avco Lycoming PLT27 | (derivative of AGT-1500 engine of XM1 tank; evaluated for LAMPS III competition) |
| T406 | Allison AE1107 | Joint(1962+): (2)V-22 |
| T407 | General Electric GE38 | Joint(1962+): [(4)P-7] |
| T408 | General Electric | (evaluated for LAMPS III competition) |
| T700 | General Electric GE12 | Joint(1962+): (2)AH-1W/Z, (2)SH-2G, (2)H-60, (2)H-61, (2)H-63, (2)H-64 |
| T701 | Allison 501-M62 | Joint(1962+): [(3)H-62] |
| T702 | Avco Lycoming LTS101 | Joint(1962+): (2)H-65 |
| T703 | Allison 250 |
(improved T63) Joint(1962+): (1)OH-58D |
| (T704) | (No information) | |
| (T705) | (No information) | |
| (T706) | (No information) | |
| (T707) | (No information) | |
| T708 | General Electric | |
| T800 | LHTEC | Joint(1962+): (2)H-66 |
| F100 | Pratt & Whitney JTF22 | Joint(1962+): (1)YA-7F, (2)F-15, (1)F-16 |
| F101 | General Electric | Joint(1962+): (4)B-1 |
| F102 | Avco Lycoming ALF502 | Joint(1962+): (2)A-9, (4)XC-8A |
| F103 | General Electric CF6 | Joint(1962+): (3)C-10, (2)C-14, (4)C-25, (4)E-4 |
| F104 | Garrett ATF3 |
Joint(1962+): (2)U-25 Missiles: (1)GQM-98 |
| F105 | Pratt & Whitney JT9D | Joint(1962+): (4)E-4A |
| F106 | Teledyne(?) | |
| F107 | Williams | Missiles: (1)AGM-86, (1)BGM-109 |
| F108 | CFM CFM56 |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (4)KC-135R/T Joint(1962+): (2)C-40, (4)E-3F, (4)E-6 |
| F109 | Garrett TFE76 | Joint(1962+): (2)T-46, [(2)T-48] |
| F110 | General Electric | Joint(1962+): (2)F-14B/D, (1)F-16C/D |
| (F111) | (No information) | |
| F112 | Williams |
Joint(1962+): (1)X-36, (1)X-50 Missiles: (1)AGM-129 |
| F113 | Rolls-Royce Mk.511 Spey | Joint(1962+): (2)C-20 |
| (F114) | (No information) | |
| (F115) | (No information) | |
| (F116) | (No information) | |
| F117 | Pratt & Whitney PW2037 | Joint(1962+): (4)C-17 |
| F118 | General Electric | Joint(1962+): (4)B-2, (1)U-2S |
| F119 | Pratt & Whitney PW5000 | Joint(1962+): (2)F-22, (2)YF-23A |
| F120 | General Electric GE37 | Joint(1962+): (2)YF-22A, (2)YF-23A |
| F121 | Williams | Missiles: (1)AGM-136 |
| F122 | Williams | Missiles: (1)AGM-137 |
| (F123) | (No information) | |
| F124 | Garrett TFE1042, TFE1088-16 |
Joint(1962+): (1)X-45A Czech Rep.: (1)Aero L-159 |
| F125 | Garrett TFE1042-70 |
(no US aircraft) Taiwan: (2)AIDC Ching Kuo |
| F126 | Rolls-Royce Mk.611/661 Tay | Joint(1962+): (2)C-20F/G/H |
| F127 | General Electric | (derivative of J101/F404 for export; cancelled) |
| F128 | General Electric | (derivative of J101/F404 for export; afterburning version of F127; cancelled) |
| F129 | Williams FJ44 | Joint(1962+): (1)Q-3 |
| F130 | Rolls-Royce BR725 | Joint(1962+): (8)B-52J |
| (F131) | (No information; probably not assigned) | |
| (F132) | (No information; probably not assigned) | |
| (F133) | (No information; probably not assigned) | |
| (F134) | (No information; probably not assigned) | |
| F135 | Pratt & Whitney | Joint(1962+): (1)F-35, (1)X-32, (1)X-35 |
| F136 | General Electric | Joint(1962+): (1)F-35 |
| F137 | Rolls-Royce/Allison AE3007H | Joint(1962+): (1)Q-4 |
| F138 | General Electric CF6-80C2L1F | Joint(1962+): (4)C-5A/B (re-engined), (4)C-5M |
| F139 | Pratt & Whitney PW4062-3 | Joint(1962+): (2)KC-46 |
| F400 | General Electric | |
| F401 | Pratt & Whitney JTF22 | Joint(1962+): (2)YF-14B, (1)FV-12 |
| F402 | Rolls-Royce Pegasus | Joint(1962+): (1)AV-8 |
| (F403) | (No information) | |
| F404 | General Electric | Joint(1962+): (2)A-6F, (2)F-18, (1)F-20, (2)F-117, (1)X-29, (1)X-31, (1)X-45B |
| F405 | Rolls-Royce/Turbomeca Adour | Joint(1962+): (1)T-45 |
| (F406) | (No information) | |
| (F407) | (No information) | |
| F408 | Teledyne CAE 382 | Missiles: (1)BQM-145 |
| (F409) | (No information) | |
| (F410) | (No information) | |
| (F411) | (No information) | |
| F412 | General Electric |
(improved F404) Joint(1962+): [(2)A-12] |
| (F413) | (No information) | |
| F414 | General Electric |
(improved F412) Joint(1962+): (2)F-18E/F |
| F415 | Williams | Missiles: (1)RGM/UGM-109E/H |
| F700 | General Electric | |
| A100 | General Electric | (proposed for F-35 engine replacement) |
| A101 | Pratt & Whitney | (proposed for F-35 engine replacement and NGAD fighter) |
| A102 | General Electric | (proposed for NGAD fighter) |
| A103 | Pratt & Whitney | (proposed for NGAD fighter) |
5.2 Rocket Engines
Rocket engines are assigned designations similar to air-breathing engines, except that the model numbering does not indicate the developing service any more. In fact, only the Air Force seems to use the LR/SR rocket designators nowadays. Navy rocket engines and motors are usually designated in the Navy's MARK/MOD numbering system, while the Army uses its Ordnance Number nomenclature.
| Examples: | X | LR | 99 | - | RM | - | 1 | |
| SR | 110 | - | AD | - | 1 | |||
| (6) | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
The letter (1) designates the type of the engine:
- LR - Liquid Fuel Rocket Engine
- SR - Solid Fuel Rocket Motor
- LSR - Liquid/Solid Hybrid Rocket
(2) is the model number of the engine. Note that there is no dash between the engine type letter and the model
number. Each rocket type uses a separate numerical sequence, starting from 1. The original method to assign odd numbers
to Air Force engines and even numbers to Navy engines has been discarded.
(3) is a two-letter code for the manufacturer of the engine. The listing of currently defined manufacturer codes can be found in the section about air-breathing engines.
The number (4) designates a specific model of the engine. Numbers are assigned in numerical sequence, starting from 1.
(5) is an optional letter for designating minor modifications of an engine model. Letters are assigned alphabetically from A on (I and O are not used).
(6) is an optional status prefix:
- X - Experimental
- Y - Service Test
Designation List:
Unfortunately, my list of rocket engine designations is still very incomplete. I don't know any actual designations in the
"LSR" series, and the SR list has numerous gaps. Therefore, I have omitted the usual "(No information)" entries for the gaps in
the latter, and have listed only designations known to me.
Because very few manned aircraft used rocket propulsion, I have ommitted the "Missiles:" designation system prefix for
all missiles listed in the "Aircraft" column.
| Designation | Manufacturer and Model | Remarks; Aircraft |
|---|---|---|
| LR1 | Aerojet 25-AL-1000 | (RATO rocket for A-20) |
| LR2 | Reaction Motors | |
| LR3 | Aerojet 25-ALD-1000 | (Droppable RATO rocket for B-25J) |
| (LR4) | (No information) | |
| LR5 | Aerojet X40-ALD-3000 | (Droppable RATO rocket) |
| LR6 | Reaction Motors | (1)SAM-N-2, (1)CTV-N-9 |
| LR7 | Aerojet XCALT-6000 | |
| LR8 | Reaction Motors |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)X-1E Other: (1)Douglas D-558-2 |
| LR9 | Aerojet X4-AL-1000 | (Brake rocket for G-4A) |
| LR10 | Reaction Motors | (1)RTV-N-12 |
| LR11 | Reaction Motors |
Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)F-91, [(1)XF-92], (1)X-1 Joint(1962+): (1)X-24 |
| (LR12) | (No information) | |
| LR13 | Aerojet X60-ALD-4000 | (RATO rocket for B-29, B-45) |
| (LR14) | (No information) | |
| LR15 | Aerojet XCNLT-1500 | |
| LR16 | Aerojet | |
| LR17 | Curtiss-Wright | (RATO rocket for XB-45) |
| (LR18) | (No information) | |
| LR19 | Curtiss-Wright | |
| LR20 | Aerojet | (1)SAM-N-2/4 |
| LR21 | Curtiss-Wright | (cancelled project) |
| LR22 | Reaction Motors | |
| LR23 | Aerojet X90-ALT-60000 | |
| LR24 | Aerojet | (1)SAM-N-2/4 |
| LR25 | Curtiss-Wright | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)X-2 |
| LR26 | Reaction Motors | |
| LR27 | Curtiss-Wright | (planned for XF-91; cancelled) |
| (LR28) | (No information) | |
| LR29 | Curtiss-Wright | (cancelled project) |
| LR30 | Reaction Motors | (planned for X-15; cancelled) |
| LR31 | M.W. Kellogg | (cancelled project) |
| LR32 | Reaction Motors | Army/AF(1924-1962): XH-15(blade-tip engine) |
| LR33 | Reaction Motors | (cancelled project) |
| LR34 | Reaction Motors | (helicopter blade-tip engine) |
| LR35 | Reaction Motors | (1)RTV-A-2 |
| (LR36) | (No information) | |
| LR37 | Curtiss-Wright | |
| (LR38) | (No information) | |
| LR39 | Reaction Motors | |
| LR40 | Reaction Motors | Navy(1922-1962): [(1)F8U-3F] |
| LR41 | North American | |
| LR42 | North American | Navy(1922-1962): (1)FJ-4F |
| LR43 | North American | Army/AF(1924-1962): [(1)X-11], [(3)X-12] |
| LR44 | Thiokol TD-174 | (1)AAM-N-6, (1)GAM-79 |
| LR45 | Aerojet AJ24-1 | (RATO rocket; planned for F-84 and cancelled B-47C(B-56)) |
| LR46 | North American | (derivative of LR42 planned for A3J) |
| LR47 | M.W. Kellogg SPD 649-1 | (RATO rocket; planned for cancelled B-47C(B-56)) |
| LR48 | Reaction Motors | |
| LR49 | Aerojet | (RATO rocket) |
| LR50 | General Electric X-405 | (1)Vanguard(1st stage) |
| LR51 | Aerojet | |
| LR52 | Aerojet AJ-10 | (1)Vanguard(2nd stage) |
| LR53 | Aerojet | (Booster rocket planned for F-80) |
| LR54 | North American | (derivative of LR42) Navy(1922-1962): [(1)F8U-1F] |
| LR55 | North American | (2.75" rocket) |
| LR56 | Aerojet | Navy(1922-1962): [(1)F8U-3F] |
| (LR57) | (No information) | |
| LR58 | Thiokol TD-187 | (1)AGM-12B, (1)AGM-83 |
| LR59 | Aerojet | (1)IM-99 |
| (LR60) | (No information) | |
| (LR61) | (No information) | |
| LR62 | Thiokol TD-232 | (1)AGM-12C/E |
| LR63 | Aerojet | (RATO/Booster rocket planned for F-84 and F-86) |
| LR64 | Rocketdyne | (1)AQM-37 |
| LR65 | Bell | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)X-9 |
| LR66 ... LR130 (even) | Most probably not assigned | |
| LR67 | Bell | (1)GAM-63 |
| (LR69) | (No information) | |
| LR71 | North American | (1)XSM-64(Booster) |
| LR73 | Aerojet | |
| LR75 | M.W. Kellogg | (RATO rocket; derivative of LR47) |
| (LR77) | (No information) | |
| LR79 | Rocketdyne S-3D | (1)SM-75(PGM-17), (1)SM-78(PGM-19) |
| LR81 | Bell | (1)RM-81 |
| LR83 | North American | [(1)XSM-64A(Booster)] |
| LR85 | Aerojet | (1)GAM-71 |
| LR87 | Aerojet | (2)SM-68(LGM-25)(1st stage) |
| LR89 | Rocketdyne | (2)SM-65(CGM-16)(Booster) |
| LR91 | Aerojet | (1)SM-68(LGM-25)(2nd stage) |
| (LR93) | (No information) | |
| (LR95) | (No information) | |
| (LR97) | (No information) | |
| LR99 | Reaction Motors | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)X-15 |
| LR101 | Rocketdyne | (2)SM-65(CGM-16)(Vernier), SM-75(PGM-17)(Vernier) |
| (LR103) | (No information) | |
| LR105 | Rocketdyne | (1)SM-65(CGM-16) |
| LR107 | Hughes Tool Co. | |
| (LR109) | (No information) | |
| (LR111) | (No information) | |
| LR113 | Aerojet | |
| LR115 | Pratt & Whitney RL-10-A-1 | (2)SSB-8 |
| (LR117) | (No information) | |
| LR119 | Pratt & Whitney RL-10-A-3 | (planned for Saturn; cancelled) |
| LR121 | Rocketdyne | Army/AF(1924-1962): (1)NF-104A |
| (LR123) | (No information) | |
| (LR125) | (No information) | |
| (LR127) | (No information) | |
| LR129 | Pratt & Whitney | (engine developed for boost/glide aerospace craft; later modified into unsuccessful competitor for Space Shuttle main engine) |
| LR132 | Rocketdyne RS-47 | ("Orbital Transfer Engine") |
| SR9 | Hercules Powder | |
| SR11 | Hercules Powder | LGM-30(Retro Motor) |
| SR13 | Lockheed | |
| SR19 | Aerojet | (1)LGM-30F/G(2nd stage) |
| SR45 | Atlantic Research | (1)PWN-6, (1)PWN-7 |
| SR47 | United Technology Center | Titan III(Zero Stage) |
| SR49 | Thiokol TU-289 | (1)AIR-2 |
| SR51 | Thiokol | LGM-25C(Retro Motor) |
| SR55 | United Technology Center | LGM-25C(Staging Motor) |
| SR59 | Atlantic Research | LGM-30(Pitch Motor) |
| SR61 | Atlantic Research | LGM-30(Spin Motor) |
| SR71 | Aerodyne | (1)PWN-8 |
| SR73 | Aerojet/Thiokol | (1)LGM-30G(3rd stage) |
| SR75 | Lockheed | (1)AGM-69, (1)ASM-135 |
| SR105 | Aerojet | (1)2.75" Improved FFAR |
| SR109 | Thiokol TX-481 | (1)AGM-65 |
| SR110 | Aerodyne | (1)PWN-10, (1)PWN-11, (1)PWN-12 |
| SR113 | Thiokol | (1)AGM-88 |
| SR114 | Thiokol TX-633 | (1)AGM-65 |
| SR115 | Aerojet | (1)AGM-65 |
| SR116 | Aerojet | (1)AIM-9J/P |
| SR118 | Thiokol | (1)LGM-118(1st stage) |
| SR119 | Aerojet | (1)LGM-118(2nd stage) |
| SR120 | Hercules | (1)LGM-118(3rd stage) |
| SR121 | Naval Propellant Plant | MQM-107(Booster) |
| SR122 | Rocketdyne |
(also designated WPU-9/B) (1)AGM-130 |
6 Sources
In no particular order:
[1] James C. Fahey: "The Ships and Aircraft of the US Fleet", 6th, 7th and 8th ed., U.S. Naval Institute, 1955, 1958, 1965
[2] James C. Fahey: "United States Air Force and United States Army Aircraft 1947-1956"
[3] James C. Fahey: "United States Army Aircraft 1908-1946"
[4] Department of Defense: MIL-STD-1812A "Aeronautical and Support Equipment Type Designation System"
[5] Gordon Swanborough, Peter M. Bowers: "United States Military Aircraft since 1908", Putnam, 1989
[6] Gordon Swanborough, Peter M. Bowers: "United States Naval Aircraft Since 1911", Putnam
[7] Bill Gunston: "World Encyclopedia Of Aero Engines"
[8] John M. Andrade: "U.S. Military Aircraft Designations and Serials 1909-1979", Midland, 1979
[9] Norman J. Bowman: "The Handbook of Rockets and Guided Missiles", Perastadion Press, 1963
[10] USAF Air Materiel Command: "Model Designations of U.S.A.F Aircraft Engines, Revised January 1, 1950"
[11] Air Force-Navy Aeronautical (ANA) Bulletin 306M: "Engines, Aircraft Turbine and Jet, Designation Of"
Comments and corrections to: Andreas Parsch
Back to Home page
Last Updated: 14 February 2024