Bureau of Standards/Goodyear SUM-N-2 Grebe
The Grebe was part of the Kingfisher family of guided anti-ship/anti-submarine weapons, which was developed under the prime contract of the National Bureau of Standards (NBS). Originally projected as Kingfisher E in 1946, it was subcontracted to Goodyear, and redesignated in September 1947 as SUM-2 (SUM-N-2 from early 1948) Grebe. Grebe was the only ship-launched missile in the Kingfisher family, the others (including the AUM-N-2 Petrel (Kingfisher C), AUM-N-4 Diver (Kingfisher D) and AUM-N-6 Puffin (Kingfisher F)) all being air-launched.
 |
| Photo: U.S. Navy |
| XSUM-N-2 (wings folded) * |
The Kingfisher E specification in 1946 called for a subsonic rocket-boosted heavy MK 35 torpedo, which was to be launched from surface ships. By 1948, the payload had been changed to a lighter MK 41 torpedo, and a long-range version with a pulsejet sustainer propulsion was also planned. The SUM-N-2 was launched in the direction of a sonar-detected target, and after a preset distance, it began its terminal dive to release its homing torpedo. Grebe was mainly intended for use against deep-diving submarines.
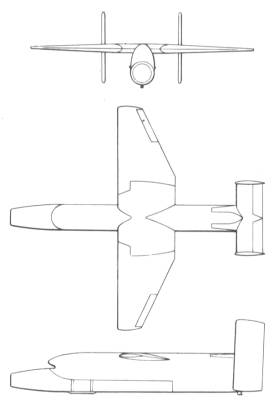 |
| Drawing: Goodyear |
| XSUM-N-2 |
Twenty XSUM-N-2 prototypes were built, and flight-tested around 1950. Grebe never became operational, reportedly because none of the then existing sonars could match the missile's range. However, the date of termination of the SUM-N-2 program is unclear, because source [1] quotes both 1950 and 1953.
Specifications
Note: Data given by several sources show slight variations. Figures given below may therefore be inaccurate!
Data for XSUM-N-2 (with pulsejet, unless noted):
| Length | 5.00 m (16 ft 5 in) |
| Wingspan | 4.27 m (14 ft) |
| Finspan | 1.52 m (5 ft) |
| Diameter | 53 m (21 in) |
| Weight | 1360 kg (3000 lb); rocket only: 1130 kg (2500 lb) |
| Speed | Mach 0.26; rocket only: Mach 0.5 |
| Range | 36500 m (40000 yds); rocket only: 4500 m (5000 yds) |
| Propulsion | Sustainer: Pulsejet; booster: solid-fueled rocket |
| Warhead | 68 kg (150 lb) high-explosive in 600 kg (1330 lb) MK 41 homing torpedo |
Main Sources
[1] Norman Friedman: "US Naval Weapons", Conway Maritime Press, 1983
[2] Frederick I. Ordway III, Ronald C. Wakeford: "International Missile and Spacecraft Guide", McGraw-Hill, 1960
[3] Bill Gunston: "The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Rockets and Missiles", Salamander Books Ltd, 1979
Back to Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles, Appendix 1
Last Updated: 2 February 2003